Real Time Twitter Stream
— Python, Twitter Streaming API, Flask — 3 min read
Introduction
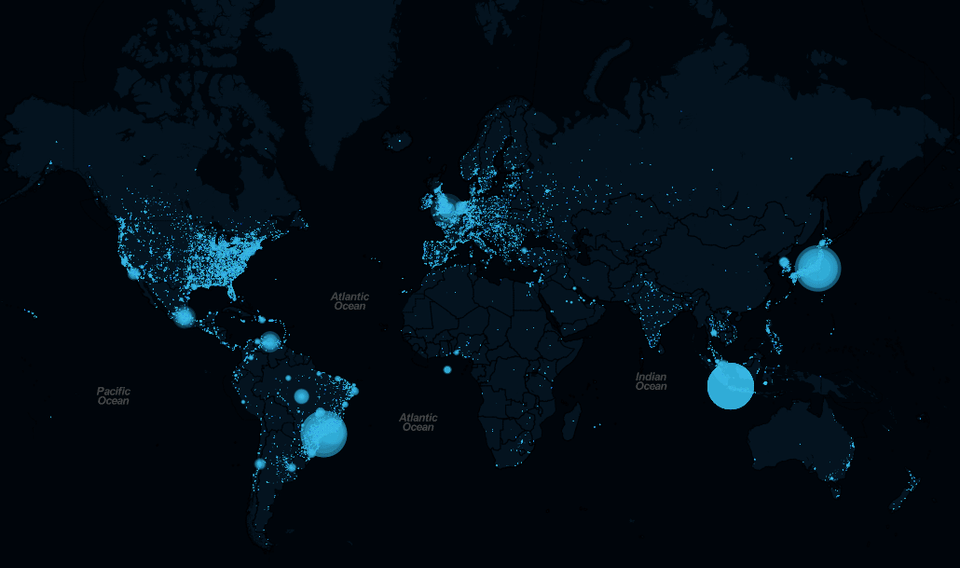
Streaming live tweets across the world in real-time on a world map. This web app attaches to the Twitter Streaming API and extracts tweets with geo data using an open-source python library Tweepy that acts as a communicator to Twitter API.
Motivation
The number of devices that translate real-world events into a constant stream of zeros and ones continues to expand faster than ever. To account for this huge influx of new data, the technology used to capture, process, and analyze this information also needs to keep up. Embracing real-time is the only option for companies seeking to elevate both the speed and the quality of information their business is analyzing.
Setup & Development
Twitter Streaming API
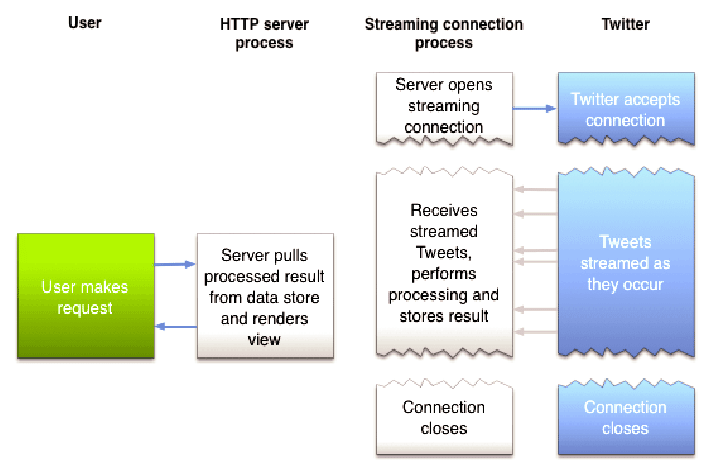
Twitter Streaming API allows you to connect to the Twitter stream of tweets. That means you can get tweets depending on some hashtags/language/location in near real-time. This API is really useful when you need to track and react, for instance, when someone mentions your company’s name. Your application can receive the tweet instantly and take action based on that tweet.
The only issue with this API is the consumption limits. The API doesn't enforce strict API limits but can stop streaming at any time. Every Twitter account can connect to a small sampling of the streaming API. This is done to guarantee users a good experience. The development of tools to spam, mislead users, and so on is forbidden. You can read more about this API here.
Invoking Twitter API with Tweepy
Tweepy is an open-source Python package that gives you a very convenient way to access the Twitter API with Python. Tweepy includes a set of classes and methods that represent Twitter’s models and API endpoints, and it transparently handles various implementation details, such as:
- Data encoding and decoding
- HTTP requests
- Results pagination
- OAuth authentication
- Rate limits
- Streams
If you weren’t using Tweepy, then you would have to deal with low-level details having to do with HTTP requests, data serialization, authentication, and rate limits. In order to connect to the stream with Tweepy, we have to set up authentication. Twitter API requires that all requests use OAuth to authenticate. These credentials are four text strings:
- Consumer key
- Consumer secret
- Access token
- Access secret
Authenticate with Twitter
Tweepy takes care of all the details for using OAuth required by the Twitter API to authenticate each request. It provides an
OAuthHandler class that you can use to set the credentials to be used in all API calls.
import tweepy
# Authenticate to Twitterauth = tweepy.OAuthHandler("CONSUMER_KEY", "CONSUMER_SECRET")auth.set_access_token("ACCESS_TOKEN", "ACCESS_TOKEN_SECRET")Create a class inheriting from StreamListener
import tweepy#override tweepy.StreamListener to add logic to on_statusclass MyStreamListener(tweepy.StreamListener):
def on_status(self, status): print(status.text)Using this class to create a Stream object passing the auth API and stream listener
myStreamListener = MyStreamListener()myStream = tweepy.Stream(auth = api.auth, listener=myStreamListenerStarting a Stream
We will use location to stream all tweets falling under the bound box.
twitterStream.filter(locations=[ -130.78125, -31.3536369415, 140.625, 63.8600358954 ])Building a Flask Server
We now create a flask server to route streaming tweets to an endpoint. We converted the incoming JSON format into GeoJSON to view it on a map.
@app.route('/data')def stream_data(): geo_data = { "type": "FeatureCollection", "features": [] } for item in data: geo_item = { "type": "Feature", "geometry": { "type": "Point", "coordinates": item['coordinates']['coordinates'] }, "properties": { "name": item["text"] }, } geo_data['features'].append(geo_item) return jsonify(geo_data)We can finally return the Flask response to be rendered by the front end leaflet map.
Summary
The project is all about building a real-time twitter stream that streams live tweets coming from across all countries and presenting it on global map in real time. It is hosted on local server built using Flask( a micro framework for Python), coded completely in Python, using Twitter’s streaming API(Twitter for Developers). The frontend map is built using the custom Leafletjs (an open source javascript library for mobile-friendly interactive maps).
You can find the entire code here.